Even when you have an attractive website filled with relevant, timely content that links to other reputable sites, there are still a few places where it’s easy to stumble and end up with negative effects on your SEO. The technical design and function of your website is just as important as the content when it comes to climbing the ranks to get a top spot on Google. One example of a technical error that can cause big problems for your search ranking is a soft 404 error.
Hard 404 Errors
A hard 404 error is something you’ve probably encountered more than once while browsing the web. Simply put, it’s a signal to a user that the page couldn’t be found or accessed. This could be because the page doesn’t exist. Hard 404 errors can be frustrating for users who can’t find a page, but aren’t likely to affect your SEO in a large way. 404 errors also aren’t always the fault of the site. If a person types in a web address wrong, for example, they may receive a hard 404 error.
Soft 404 Errors
Soft 404 errors, on the other hand, are negative signals for your website. A soft 404 error occurs when someone is trying to access a URL on your website and is getting a message that the page doesn’t exist. However, the site isn’t sending out a typical 404 error code. Instead, it’s responding with a 200 OK HTTP response code. This means that the site is saying the URL is fine and not broken or missing. In other words, the response indicates a successful HTTP request. When the request isn’t successful, the 200 OK code shouldn’t be sent by the server. When soft 404 errors appear on a large percentage of your pages, it becomes a serious customer experience and SEO issue.
Effects on Page Indexing
When Googlebot crawls the web to index pages, it has a limited amount of time that it can spend on each domain before it moves on to another one. When you have pages giving soft 404 errors, Googlebot interprets them as pages with unique content that you want indexed and displayed in search results. So it spends some of the time it has on your domain to index pages that aren’t delivering unique or useful content to your viewers. This is sometimes called a sites crawl budget.
This means that the pages you want indexed may take longer to update and rank on Google. You should run your website so that you have the best chance of ranking for the keywords you’re targeting as quickly as you can—and soft 404 errors can prevent that from happening. Instead you may be ranking for useless terms that aren’t related to your niche, especially if you have a high proportion of pages with 404 errors.
Effects on SEO
Because a soft 404 error can limit the number of good pages indexed and how frequently they’re indexed, it can have a negative effect on your SEO. Ideally, every time Googlebot crawled your page it would index the newest versions of all your pages, signaling to Google’s ranking algorithm that you’re a frequently-updated and relevant site. However, when your pages with soft 404 errors are indexed, you’re losing the positive benefits of all those well-crafted, on target pages. This is because the web crawlers may not prioritize the pages you’re trying to rank when they’re spending their time on pages with soft 404 errors.
Google on Soft 404 Errors
Google directly said on the Webmaster Central Blog that:
“We discourage the use of so-called “soft 404s” because they can be a confusing experience for users and search engines. [. . .] Search engines may spend much of their time crawling and indexing non-existent, often duplicative URLs on your site. This can negatively impact your site’s crawl coverage.”
There are some areas of SEO like subfolders vs subdomains where Google isn’t extremely clear on what you should do to get the best possible SEO results. However when Google is direct and clear about an issue, you should always do what they suggest. In the case of soft 404 errors, your best bet is to eliminate them completely so that you have the highest ranking you can achieve.
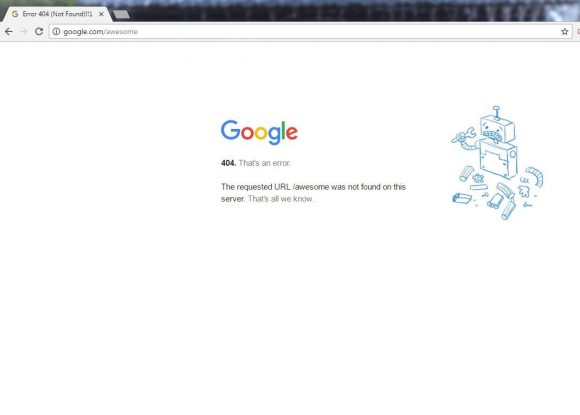
Example of a hard 404 error page.
User Experience
Another problem with soft 404 errors is that they create a negative and confusing user experience. A hard 404 error just refuses to load the content and explains that it couldn’t be found. However, a soft 404 will often redirect to the homepage or show a related page that wasn’t what the user was searching for. It can be a frustrating experience for a person looking for content on your site and may end up preventing a return visit from that person in the future.
You don’t have to use the standard 404 error page either. You can create a custom page that is triggered when someone requests a page that doesn’t exist on your server. It can redirect the user to another page while still sending the 404 error code out that indicates that the page isn’t found. This is one way to improve the experience for users of your website.
Configuring Your Pages
When you have a URL for a page that isn’t there anymore, it’s best to configure it to return a hard 404 error. This tells both users and search engines that the file couldn’t be found.
Even if your page is displaying a 404 error message, it may not be actually transmitting a 404 error code. The code and the content of the page aren’t necessarily the same. Your page must be transmitting that code so that Google and users know that it’s nonexistent or not reachable. The HTTP header response must be changed so that the server returns a proper 404 code instead of the 200 OK code.
301 Redirects
One way to deal with a page that is no longer available is to configure it to redirect to a different page. However, if you’re not planning to revamp the page in the future and if it doesn’t have value in terms of entry traffic, it’s better to completely delete it and move it off your sitemap for good. That way Google will stop indexing that URL and spend its time crawling pages that still offer good information.
Another reason to use a redirect is if you have a valuable link on another site that you don’t want to lose. The link will still be directed to its original page, and then the 301 code will bring it to the new page. It can preserve your very high-value SEO links.
Never try to configure your site to only use 301 redirects instead of 404s. They’re only appropriate when a direct replacement page is available. Some webmasters turn every 404 into a redirect, but that’s not an appropriate way to set up your website. Having 404 errors when no direct replacement product or page is available is more appropriate.
How to Check For Soft 404 Errors
The first thing you need to do is see how many of your pages are returning soft 404 error codes. Load your site into Google Webmaster Tools (or Search Console as its actually called now but I still prefer the old name!) and navigate to the Diagnostics portion of the page. Once there, open Crawl Errors and look to see what pages, if any, are returning errors. Above the listed URLs, click Soft 404s to see which pages Google thinks are soft 404 errors.
Sometimes Googlebot believes a page is a soft 404, but it’s really a page with accurate content returning a 200 OK response. In that case, it’s good to have the page indexed and you don’t need to worry about the code. Other times, you need to configure the page so that it 301 redirects to the right page. (For example, if you were running a contest that ended but you’re still getting hits on that page and want to steer them to a new contest or information about your products.)
If the page shouldn’t exist or should be returning a 404 error code, then it’s time to fix the problem.

Fixing Pages with the Wrong HTTP Response Code
If your page is returning the wrong error code and you want to change it, talk to the person who handles your website. They’ll have to update the code in the content management system for each of the URLs in question. Depending on which content management system or website architecture you use, the fix will vary.
Useful Tools
Once you’ve fixed any errors in how Google and site visitors see your page, try using Fetch as Google. It’s a useful tool that can give you insight into how Google crawls your page and whether anything on it is blocked to the crawler. If you have anything you need to debug, Fetch as Google is a good place to start and will let you see what, if any, errors exist in the indexing process.
If you aren’t sure what HTTP status codes are being sent by a URL, use a tool to find out. One web-based tools that can help is the HTTP Status Code Checker. It will shed light on which codes a particular URL is giving. The more information you have about how Google reads, indexes and displays your site, the better you can optimize it to get the best possible SEO.
Creating a Custom 404 Page
Once you’ve sorted out your soft 404 errors, you should create a custom 404 page to help site visitors navigate to the information they want or need. Ideally, the page would give them navigation options, an error message and any additional information you deem fit in an attractive format that fits with the rest of your site. Having a custom page could help retain first-time visitors who navigate to your site and are met with an error. Google offers a 404 widget you can place on a custom 404 page. It not only helps a viewer find more information, but also suggests other ways to find what they clicked the link to find.

Github have combined custom visuals with humour for a great 404 page
You can use your Google Webmaster account to check the XML sitemap of your page to make sure the widget will display and function correctly.
Making it easier for a viewer to find what they want may increase the likelihood that the person will stay on your page instead of switching to a competitor. They will offer a way back to your primary domain and also give you protection against undiscovered broken links.
Though soft 404 errors may not look like a major problem for your site, they can have a major impact on both the search engine ranking and the customer experience. Identifying, locating and adjusting your pages so that the right HTTP code is sent can fix these problems. Since your search ranking goes a long way in determining how much traffic is sent to your site by Google, it’s essential to optimize your pages and deliver the best possible product to both site visitors and web crawlers.



Awesome Post ! Thank you for sharing
Hi David,
Very good to found this post explains the differences between soft 404 Vs hard 404
Errors. I didn’t know whenever I saw such errors. But today finally you have explored it to me.
Good to know it’s effects on SEO and page indexing, having the information about it supposed to be very useful in coming time.
You are definitely right, 404 errors create a negative and confusing experience to user, I do confused and feel tedious solving it.
I’m so happy to know the use of tool HTTPstatus checker.
Thanks for sharing.
– Ravi.